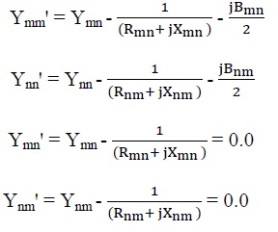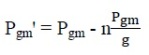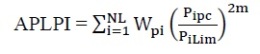INTRODUCTION
Contingency analyses are important tasks for the safe operation of electrical energy network. Potential harmful disturbances that occur during the steady state operation of a power system are known as contingencies. Contingency analysis is carried out by using repeated load flow solutions for each of a list of potential component failures. This process has to be executed for all the possible contingencies, and repeated every time when the system load or structure changes significantly. Conventional methods are tedious and time consuming process, which is not desirable for real time applications. Various approximate methods have been proposed already for real time static security analysis of power systems. These methods reduce computational effort but they may not classify system contingencies accurately.
Power Systems are operated so that overload do not occur either in real-time or under any statistically likely contingency. This is often called maintaining security. Steady state power system insecurity such as transmission lines being overloaded causes transmission elements cascade outages which may lead to complete blackout. The power system operator must know the system state at any instant. The contingency analysis is used to predict which contingencies make system violations and rank the contingencies according to their relative severity. Contingency Analysis is useful both in the network design stages and for programmed maintenance or network expansion works to detect network weaknesses. The weaknesses can be strengthened by transmission capacity increase, transformers rating increase besides circuit breakers ratings increase. The AC load flow analysis used to perform contingency analysis can be termed AC contingency analysis routine. The advantage of AC contingency analysis routine is that it provides the post outage power factor of the branch power flows besides detecting the bus voltage limit violations post contingencies. Probability of single contingencies occurrence is higher than that of multiple contingencies occurrence, but for maintenance and transmission system expansion, scheduled and planned outages may include dropping out of multiple elements. Thus it is important to study multiple outages effect as well as single outages.
Analysis of Transmission Line Outage
The formulation of corresponding bus admittance matrix is essential for simulation of transmission line outage. The outage of line tied with bus ‘m’ and ‘n’ will affect the Ymm, Ymn Ynm and Ynn element of admittance [Y] matrix. The new values of those admittances for the (π) mode of representation of transmission lines are given by equation shown below:
where,
Analysis of Generating Unit Outage
This approach only analyzes the outage of one unit (or more) in a generating station. Let the total generation for the station at
bus (m) be Pgm, and assume there exist identical (g) units, then power generated at bus ‘m’ after the outage is given by equation shown below:
Active Power Loading Performance Index (APLPI)
APLPI is the active power loading performance index corresponding to line real power flow violations. It is formulated as shown in equation below, and gives measure of line MW overloads.
Ranking of Contingencies
Generally, power system engineers use their past experiences in order to judge the system contingencies, which may be inappropriate for analyzing severe contingencies. Therefore, the development ofa contingency ranking algorithm which would
rank contingencies based upon their relative severity is desirable.The contingencies can be ranked based upon their effects on line loading or bus voltages.
A variety of algorithms are developed which can be classified into two groups. One is the performance index (PI) based method which utilizes a wide system scalar performance index to quantify the severity of each case by calculating their PI values and ranking them accordingly. The other is the screening method which is based on approximate power flow solutions to eliminate those noncritical
contingencies. With the advancement of artificial intelligence, expert systems and fuzzy theory are proposed to estimate the severity of various contingencies. Also artificial neural networks approaches based on (PI) have been proposed for contingency selection. In this study contingencies are ranked using a PI based method.
The ranking method used in this paper is a fast and accurate method to rank the contingencies according to their severity on
the power system. Contingencies are ranked in the order of their performance index values and processed starting with the most severe contingency at the top of the list proceeding down the ranking to the less severe ones. The exponent (m) of the performance index is changed in the range from 2 to 30 to avoid masking errors. Outages are then ranked on the basis of their corresponding performance indices. A contingency may be severe in the point view of line loading but do not affect the system bus voltages and vice- versa.